基于blockedSample的on-cpu和off-cpu的联合热点分析调优实践
发表于 2025/09/11
0
作者 | 雷世龙
一、介绍
在对应用进行性能优化的场景下,用户往往需要对应用的热点函数进行识别,基于占比最高的热点函数所在的位置去做对应的优化,来带来最大的性能提升。但业界现有的工具往往只能识别进程处于on cpu态的热点(比如perf),而如果应用的性能瓶颈在off cpu上,针对on cpu的热点去进行优化,往往无法带来性能提升,需要采用专门的off cpu采集工具去进行分析,此时又缺乏on cpu的数据,无法直接分析性能优化的效果,且一些off cpu工具只能给出程序处于off cpu的时间占比,没有对应的调用栈无法获知进程陷入off cpu的原因,比如bcc工具集中的offtime工具。
libkperf的IO和计算热点混合采样(Blocked Sample)能力可以同时对进程的on cpu和off cpu数据进行采集,且通过采集的调用栈可以获知进程进入off cpu的原因,从而可以进行针对性的性能优化。
二、工具使用
libkperf库的编译安装可以参考:https://gitee.com/openeuler/libkperf
git clone --recurse-submodules https://gitee.com/openeuler/libkperf.git
cd libkperf
bash build.shblockedSample能力详细使用教程:https://gitee.com/openeuler/libkperf/blob/master/docs/Details_Usage.md
三、案例
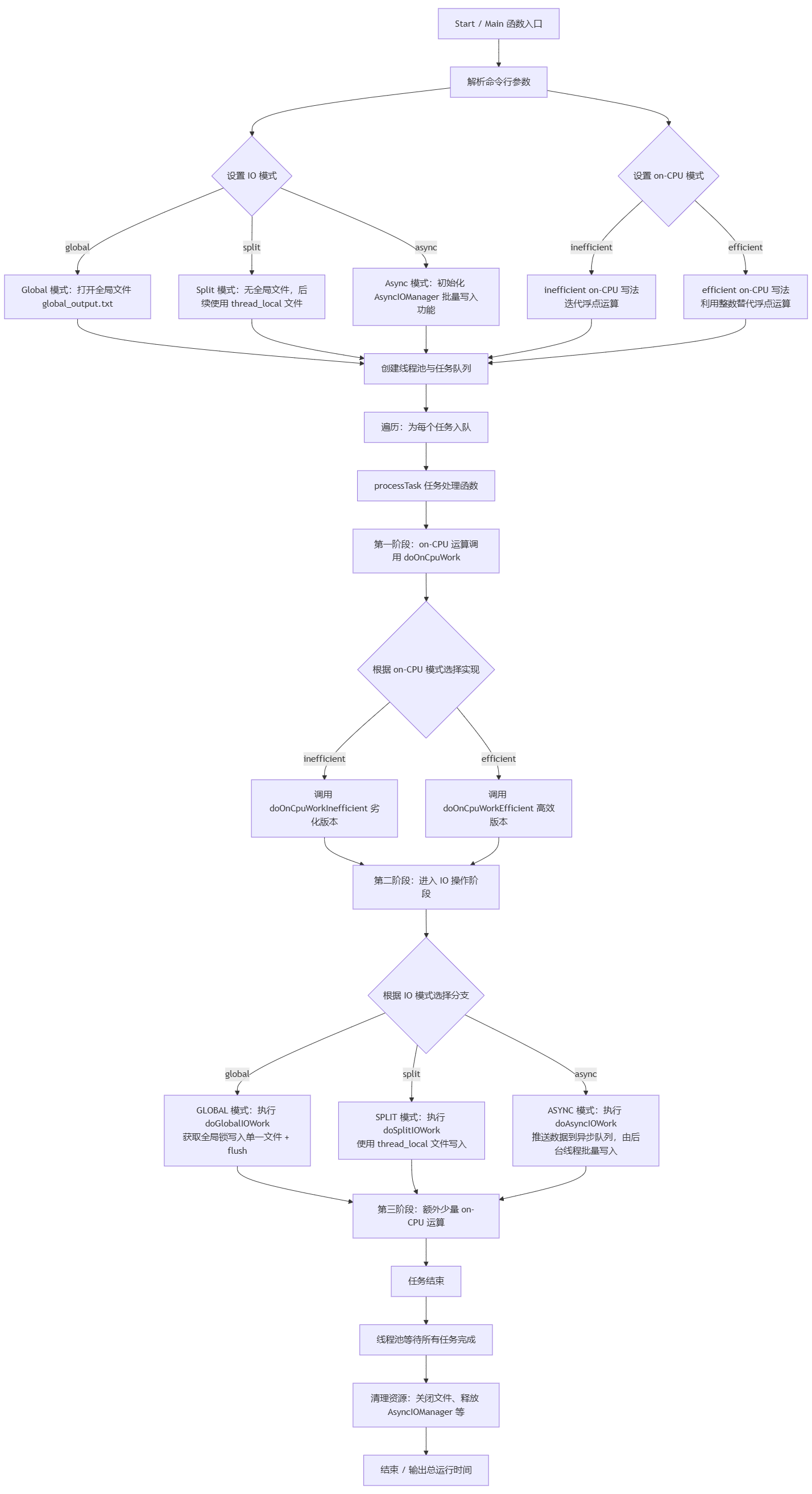
1、样例程序构造
任务设计:每个任务都会先进行一定量的on cpu工作(通过大量浮点运算模拟CPU密集型计算),然后进入off cpu阶段,通过向一个全局的共享文件写入大量的数据。并且该文件写入操作由一个全局互斥锁保护,因而会产生严重的锁竞争,来模拟实际应用中可能遇到的同步IO阻塞。接着,再进行少量计算,模拟进入on cpu的计算任务。
多线程设计:设计一个简单的线程池来模拟实际应用中的多线程执行。线程池内部有一个任务队列,多个worker线程不断从队列中取出任务执行。
支持可配置关键参数说明:
-
numThreads: 工作线程数(默认为4)
-
tasksPerThread:每个线程需要处理的任务数(默认为50)
-
cpuIterations:on-CPU计算迭代次数(默认为100000)
-
ioDataSize:单次IO写入数据字符数(默认为5000)
-
ioWrites:单任务IO操作次数(默认为3000)
-
ioMode:提供三种工作模式
-
global模式(基线):使用全局互斥锁保护同一个文件写入,容易出现锁竞争。
-
split模式:每个线程使用线程局部的输出文件,将全局锁竞争降至最低,优化程序性能。
-
async模式:每个任务采用异步io进行优化,并采用批量写的方式,优化锁竞争,来提升性能。
-
-
onCpuMode:提供两种工作模式
-
inefficient模式(基线):大量浮点计算模拟CPU密集型计算任务。
-
efficient模式:采用整数替代浮点数运算,优化on cpu的计算效率。
-
用例的流程图:
2、实验验证分析
编译参考进程示例:
g++ -g -o blocked_sample_case blocked_sample_case.cpp -lpthread
采用默认参数执行目标进程输出:
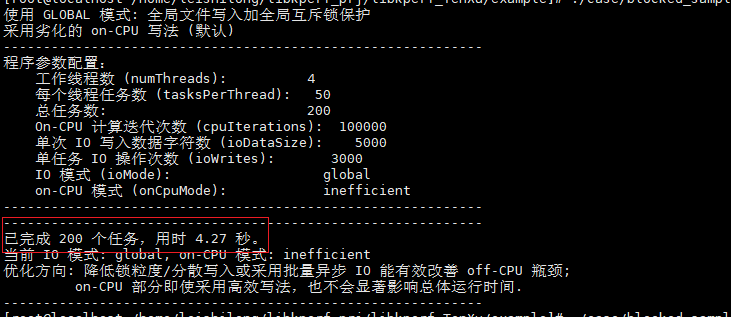
采用perf record分析此进程的热点,输出结果如下:
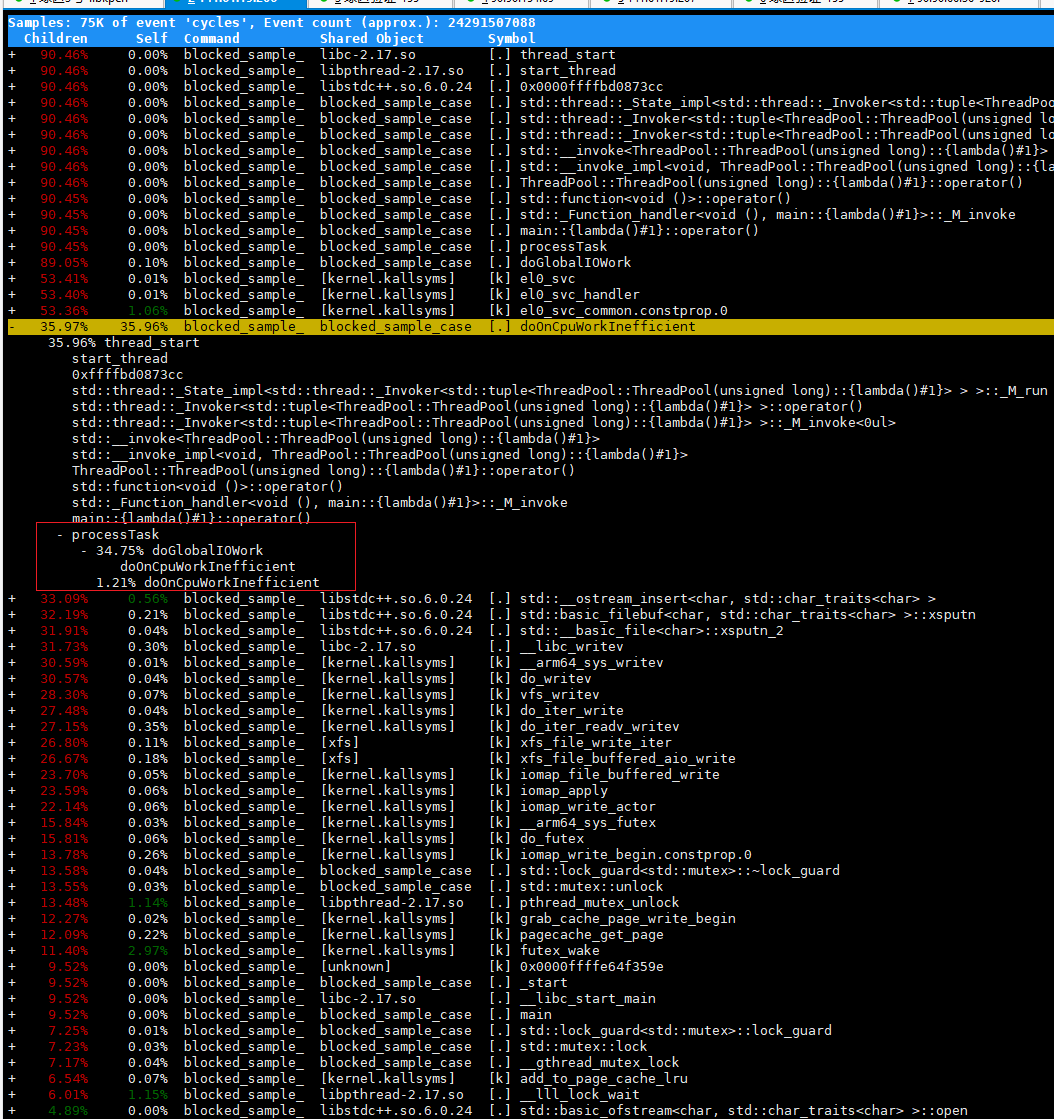
由热点分布可知,此时主要的热点在on cpu上,对on cpu进行优化:
./case/blocked_sample_case 4 50 100000 5000 3000 global efficient
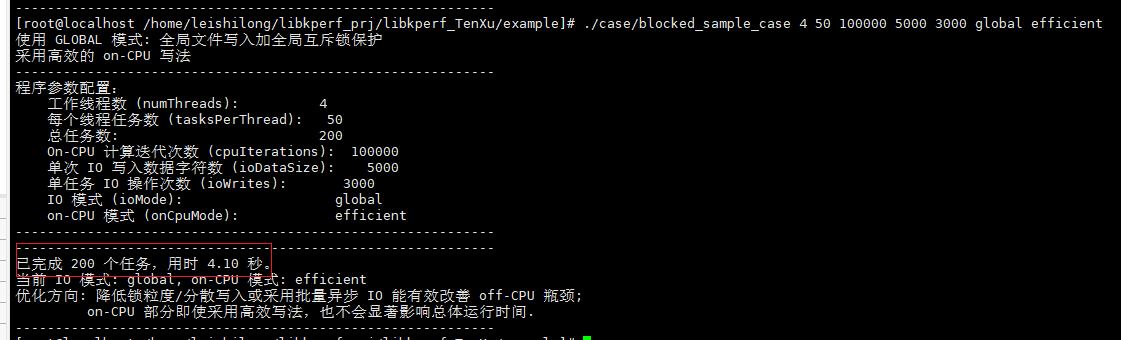
如果直接根据perf record识别出的热点,发现采用更高效的写法,性能的优化不是很明显,都有可能是程序的波动,这会造成错误的优化方向。
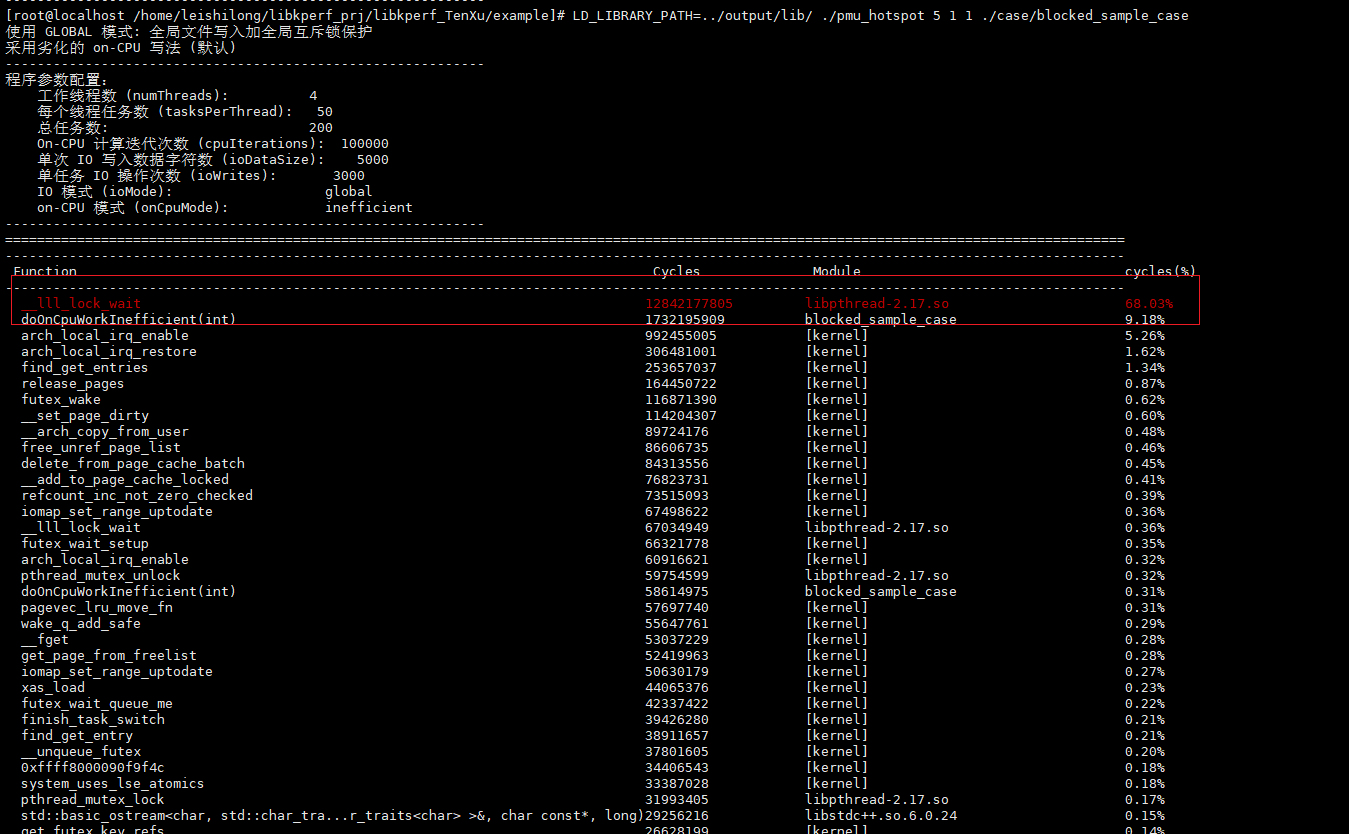
如果使用libkperf的blockedSample去采集:
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=../output/lib/ ./pmu_hotspot 5 1 1 ./case/blocked_sample_case
绘制的热点函数分布图:
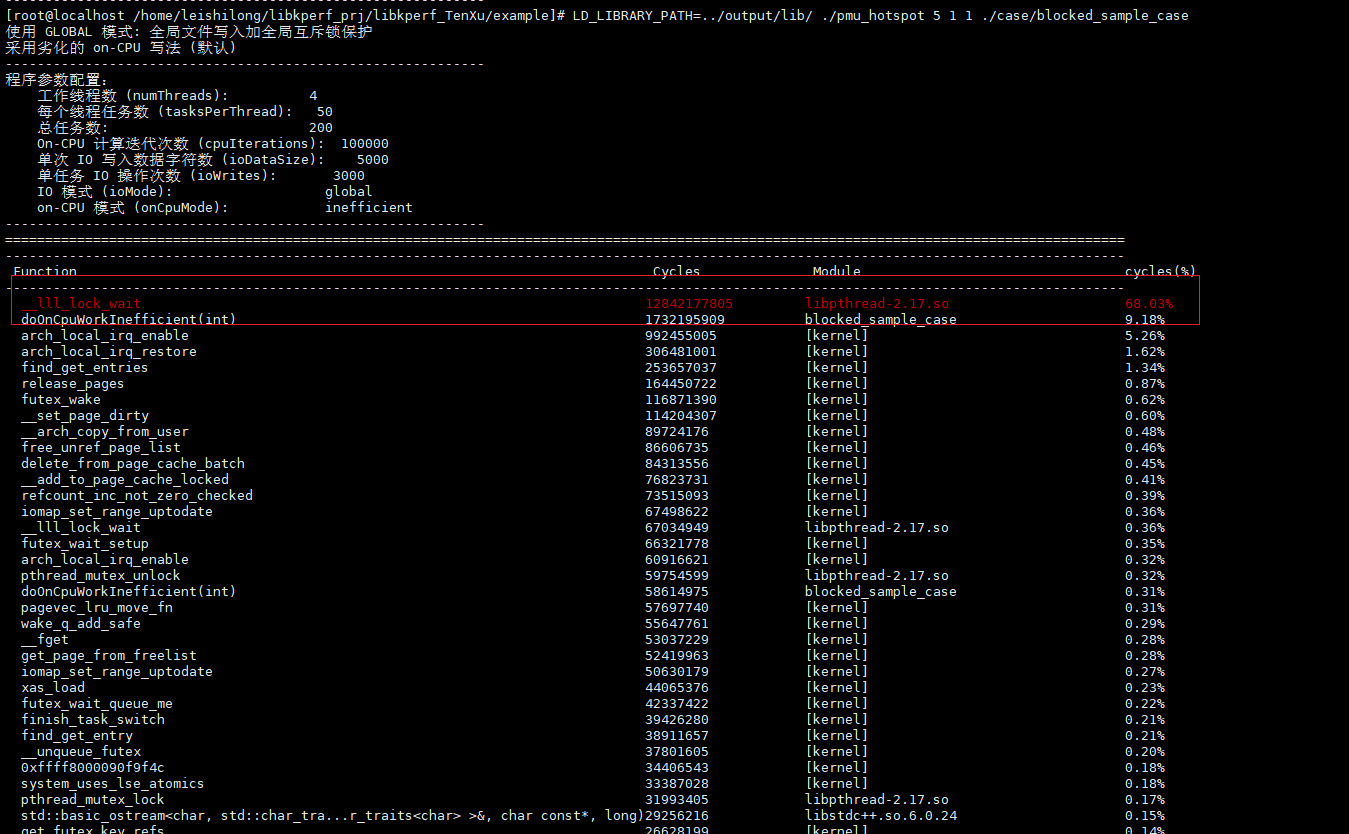
打印的调用栈:
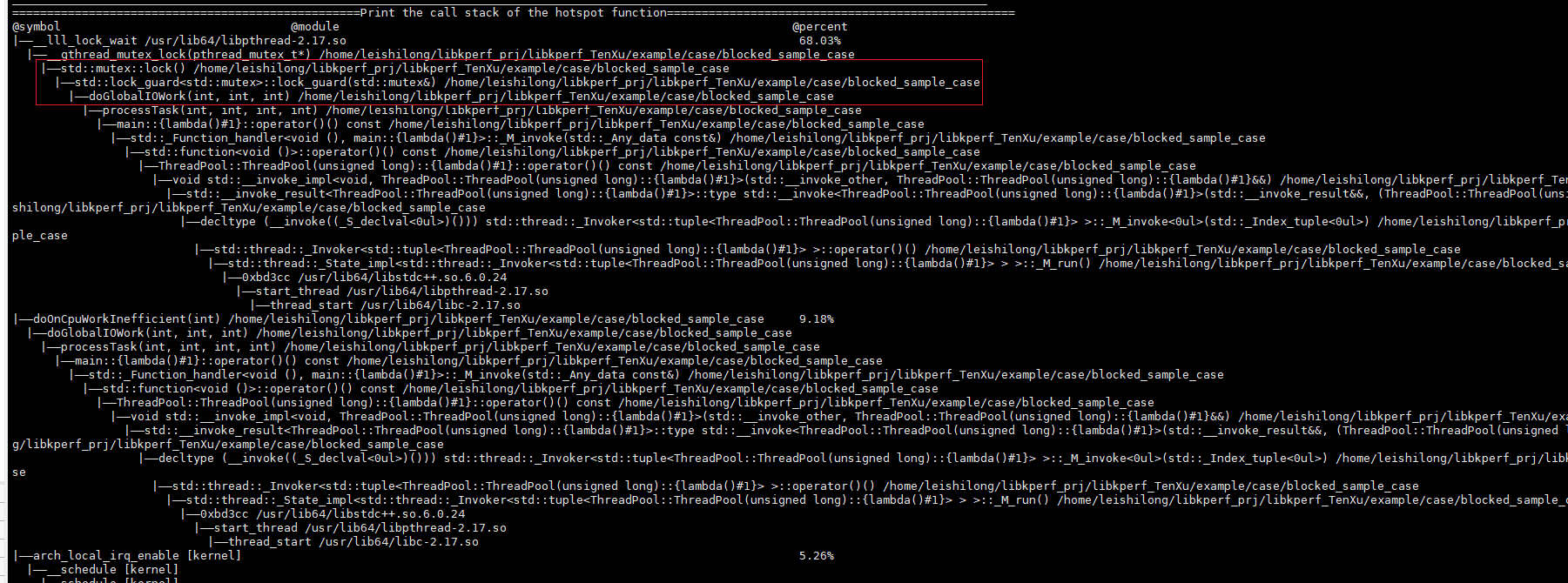
根据此时的热点计算和对应的调用分析可以准确的识别,当前样例程序的真实热点是由于锁竞争造成的,且占据程序运行时间高达68%,因此,如果去优化IO的写法可以带来极大的性能提升。
改写验证,将IO操作改成split模式运行用例:
./case/blocked_sample_case 4 50 100000 5000 3000 split
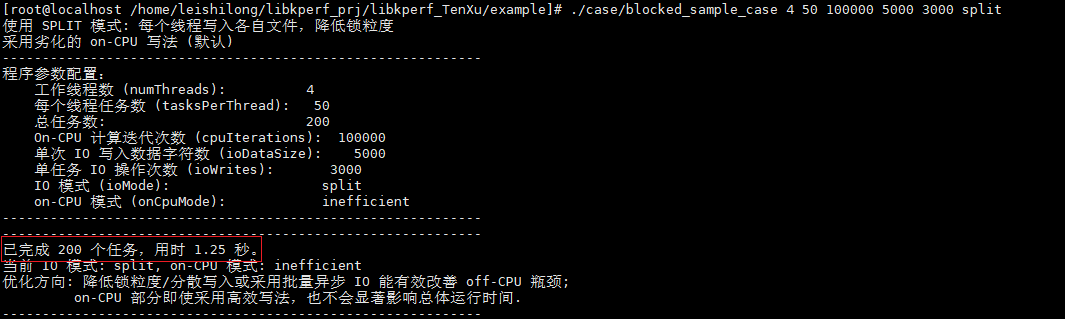
从结果来看,改进IO操作的写法可以带来极大的性能提升。
再次采集此时的热点:
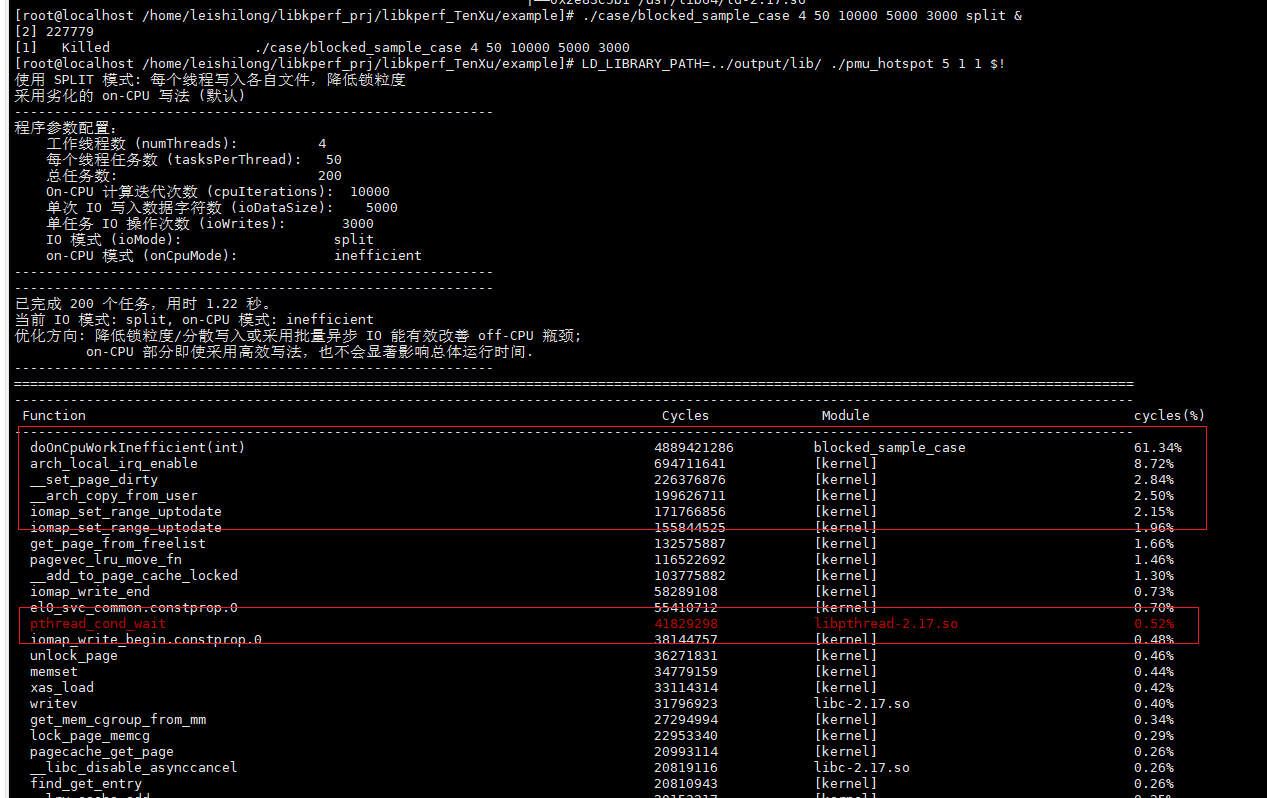
可以发现标红的由于off cpu的热点出现了极大的下降,说明上述优化锁竞争的方法有效性。
如果采用异步IO的方法来对采集进行优化。
./case/blocked_sample_case 4 50 100000 5000 3000 async
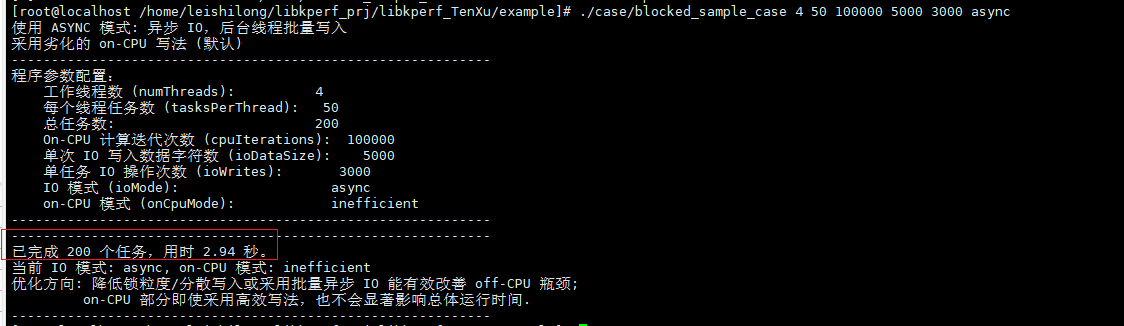
此方案也可以带来性能优化,但是优化效果没有split方案高。
从采集的调用栈的热点分析可知,此方案的优化还存在较高的条件变量竞争问题,因此,性能优化效果相比split改进方案更差一点。
3、实验结论与作用
-
准确识别应用热点瓶颈:
采用blockedSample的热点分析可以帮助用户更加准确的定位当前应用的热点,识别正确的优化方向。比如用例通过优化off cpu的代码可以更好的带来性能提升,而on cpu的优化性能提升较低。
-
对比不同优化方案的提升效果:
采用blockedSample的热点分析也可以用于对比不同优化方案带来效果差异的原因。比如用例中两种改写全局锁竞争的方案,采用线程局部输出(split模式)比异步IO的效果更好。
-
对比分析
两者的热点函数图可知在异步IO方案下,还存在大量的条件变量竞争的问题,且占比最高,说明优化效果低一些;而split方案下处于off cpu的条目已经不是最高热点了,基本消除了锁竞争的问题,效果更好。
4、附录
/*
* 优化说明:
*
* 本程序构造了一个多线程任务,每个任务包含三个阶段:
*
* 1. on-CPU 运算:
* 提供两种模式:
* - inefficient :使用大量浮点运算模拟低效计算(默认)。
* - efficient :采用整数替代浮点数运行,优化计算效率(尽管更高效,但整体时间变化不大,
* 因为 off-CPU 阶段(同步 IO)才是主导瓶颈)。
*
* 2. IO 操作阶段:
* 提供三种模式:
* - global : 全局锁保护写入单一文件(基线)。
* - split : 每个线程写到自己的文件(降低锁竞争)。
* - async : 异步 IO,将数据入队,由后台线程批量写入(前一版本未批量导致性能反而较差)。
*
* 3. 补充少量 on-CPU 运算。
*
* 使用方法(命令行参数顺序):
* [numThreads] [tasksPerThread] [cpuIterations] [ioDataSize] [ioWrites] [ioMode] [onCpuMode]
*
* 示例(你给定的测试参数,加上 onCpuMode 参数):
* ./blocked_sample_io 4 50 100000 5000 3000 global inefficient
*
* 其中:
* ioMode:global|split|async
* onCpuMode:inefficient(劣化写法) 或 efficient(高效写法)
*
* 注意:如果用户尝试用高效 on-CPU 写法优化 CPU 计算部分,整体运行时间几乎不变,
* 证明瓶颈主要在 off-CPU 部分(同步 IO 和锁竞争)。
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
#include <chrono>
#include <atomic>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <cmath> // 用于 std::pow
using namespace std;
using namespace std::chrono;
// 定义 IO 模式枚举
enum class IOMode { GLOBAL, SPLIT, ASYNC };
IOMode currentIOMode = IOMode::GLOBAL; // 默认 IO 模式
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// on-CPU 模拟部分:两种计算方式的实现
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// 劣化的 CPU 工作:大量循环计算,防止编译器优化
void doOnCpuWorkInefficient(int iterations) {
volatile double dummy = 1.0;
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++) {
dummy = dummy * 1.000001 + 0.000001;
}
(void)dummy;
}
// 高效的 CPU 工作:利用整数模拟小数优化计算
void doOnCpuWorkEfficient(int iterations) {
long long dummy = 1000000; // 用整数模拟小数,假设精度为 1e-6
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++) {
dummy = dummy * 1000001 / 1000000 + 1;
}
(void)dummy;
}
// 全局标志,决定使用哪种 on-CPU 计算方式(默认劣化写法)
bool efficientOnCpu = false;
// 封装后的 on-CPU 工作接口,根据 efficientOnCpu 调用对应实现
void doOnCpuWork(int iterations) {
if (efficientOnCpu)
doOnCpuWorkEfficient(iterations);
else
doOnCpuWorkInefficient(iterations);
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// GLOBAL 模式下的全局文件与互斥锁
//-------------------------------------------------------------
mutex globalFileMutex;
ofstream globalSyncFile; // 全局文件
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// 异步 IO 管理器(优化版):采用批量写入减少 flush 次数
//-------------------------------------------------------------
class AsyncIOManager {
private:
queue<string> msgQueue;
mutex mtx;
condition_variable cv;
atomic<bool> stop;
thread worker;
ofstream outFile;
const size_t batchSize; // 每次批量写入的消息数量
public:
AsyncIOManager(const string& filename, size_t batchSize = 50)
: stop(false), batchSize(batchSize)
{
outFile.open(filename, ios::out | ios::trunc);
if (!outFile.is_open()){
cerr << "无法打开文件: " << filename << endl;
}
worker = thread([this]() { this->process(); });
}
~AsyncIOManager(){
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock(mtx);
stop = true;
}
cv.notify_one();
if(worker.joinable()){
worker.join();
}
if(outFile.is_open()){
outFile.close();
}
}
// 将待写消息推入队列
void push(const string &msg) {
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock(mtx);
msgQueue.push(msg);
}
cv.notify_one();
}
private:
// 后台线程批量处理写入操作
void process() {
while (true) {
vector<string> localBatch;
{
unique_lock<mutex> lock(mtx);
cv.wait(lock, [this]() { return stop || !msgQueue.empty(); });
while (!msgQueue.empty() && localBatch.size() < batchSize) {
localBatch.push_back(msgQueue.front());
msgQueue.pop();
}
if (stop && localBatch.empty()) {
break;
}
}
// 批量合并写入后 flush
if (outFile.is_open()) {
string batchStr;
for (const auto &msg : localBatch) {
batchStr.append(msg);
}
outFile << batchStr;
outFile.flush();
}
}
}
};
AsyncIOManager *asyncIO = nullptr; // 全局异步 IO 管理器指针
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// 线程池:管理工作线程及任务队列
//-------------------------------------------------------------
class ThreadPool {
public:
ThreadPool(size_t threads);
~ThreadPool();
void enqueue(function<void()> task);
void wait();
private:
vector<thread> workers;
queue<function<void()>> tasks;
mutex queue_mutex;
condition_variable condition;
atomic<bool> stop;
atomic<int> active_tasks;
condition_variable cv_finished;
};
ThreadPool::ThreadPool(size_t threads) : stop(false), active_tasks(0) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < threads; i++) {
workers.emplace_back([this, i]() {
while (true) {
function<void()> task;
{
unique_lock<mutex> lock(this->queue_mutex);
this->condition.wait(lock, [this]() {
return this->stop.load() || !this->tasks.empty();
});
if (this->stop.load() && this->tasks.empty())
return;
task = move(this->tasks.front());
this->tasks.pop();
active_tasks++;
}
task();
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock(this->queue_mutex);
active_tasks--;
if (tasks.empty() && active_tasks == 0) {
cv_finished.notify_all();
}
}
}
});
}
}
ThreadPool::~ThreadPool() {
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock(queue_mutex);
stop.store(true);
}
condition.notify_all();
for (thread &worker : workers) {
if (worker.joinable())
worker.join();
}
}
void ThreadPool::enqueue(function<void()> task) {
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock(queue_mutex);
tasks.push(move(task));
}
condition.notify_one();
}
void ThreadPool::wait() {
unique_lock<mutex> lock(queue_mutex);
cv_finished.wait(lock, [this]() {
return tasks.empty() && active_tasks == 0;
});
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// 辅助函数:打印分隔线和参数说明
//-------------------------------------------------------------
void printDivider() {
cout << string(60, '-') << endl;
}
void printUsage(const char* programName) {
cout << "Usage: " << programName << " [numThreads] [tasksPerThread] [cpuIterations] [ioDataSize] [ioWrites] [ioMode] [onCpuMode]" << endl;
cout << " numThreads: 工作线程数 (默认值:4)" << endl;
cout << " tasksPerThread: 每个线程任务数 (默认值:50)" << endl;
cout << " cpuIterations: on-CPU 计算迭代次数 (默认值:100000)" << endl;
cout << " ioDataSize: 每次同步 IO 写入的数据字符数 (默认值:5000)" << endl;
cout << " ioWrites: 同一任务中进行 IO 操作次数 (默认值:3000)" << endl;
cout << " ioMode: IO 模式,可选值:global, split, async (默认:global)" << endl;
cout << " onCpuMode: on-CPU 模式,可选值:inefficient, efficient (默认:inefficient)" << endl;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// GLOBAL 模式下的 IO 操作:全局锁写入同一文件
//-------------------------------------------------------------
void doGlobalIOWork(int taskId, int ioDataSize, int ioWrites) {
stringstream ss;
ss << "Task " << taskId << " data: ";
for (int i = 0; i < ioDataSize; i++) {
ss << "X";
}
ss << "\n";
string data = ss.str();
for (int i = 0; i < ioWrites; i++) {
{
lock_guard<mutex> lock(globalFileMutex);
if (globalSyncFile.is_open()) {
globalSyncFile << data;
globalSyncFile.flush();
}
}
doOnCpuWork(1000);
}
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// SPLIT 模式下的 IO 操作:每个线程写入各自文件
//-------------------------------------------------------------
void doSplitIOWork(int taskId, int ioDataSize, int ioWrites) {
stringstream ss;
ss << "Task " << taskId << " data: ";
for (int i = 0; i < ioDataSize; i++) {
ss << "X";
}
ss << "\n";
string data = ss.str();
static thread_local ofstream localFile;
static thread_local bool initialized = false;
if (!initialized) {
auto tid = this_thread::get_id();
hash<thread::id> hasher;
size_t id_hash = hasher(tid);
string filename = "split_output_" + to_string(id_hash) + ".txt";
localFile.open(filename, ios::out | ios::trunc);
if (!localFile.is_open()) {
cerr << "无法打开文件: " << filename << endl;
}
initialized = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < ioWrites; i++) {
localFile << data;
localFile.flush();
doOnCpuWork(1000);
}
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// ASYNC 模式下的 IO 操作:将数据推入异步队列
//-------------------------------------------------------------
void doAsyncIOWork(int taskId, int ioDataSize, int ioWrites) {
stringstream ss;
ss << "Task " << taskId << " data: ";
for (int i = 0; i < ioDataSize; i++) {
ss << "X";
}
ss << "\n";
string data = ss.str();
for (int i = 0; i < ioWrites; i++) {
if (asyncIO) {
asyncIO->push(data);
}
doOnCpuWork(1000);
}
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// 每个任务的处理过程:on-CPU 计算 -> IO 操作 -> 补充少量 on-CPU 计算
//-------------------------------------------------------------
void processTask(int taskId, int cpuIterations, int ioDataSize, int ioWrites) {
// 第一阶段:on-CPU 运算(根据 onCpuMode 选择实现)
doOnCpuWork(cpuIterations);
// 第二阶段:IO 操作,根据当前 IO 模式选择执行方式
if (currentIOMode == IOMode::GLOBAL) {
doGlobalIOWork(taskId, ioDataSize, ioWrites);
} else if (currentIOMode == IOMode::SPLIT) {
doSplitIOWork(taskId, ioDataSize, ioWrites);
} else if (currentIOMode == IOMode::ASYNC) {
doAsyncIOWork(taskId, ioDataSize, ioWrites);
}
// 第三阶段:额外少量 on-CPU 运算
doOnCpuWork(cpuIterations / 10);
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// main 函数:解析参数、初始化 IO & on-CPU 模式、启动线程池并统计耗时
//-------------------------------------------------------------
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// 默认参数
int numThreads = 4;
int tasksPerThread = 50;
int cpuIterations = 100000;
int ioDataSize = 5000;
int ioWrites = 3000;
string ioModeStr = "global"; // 默认 IO 模式
string onCpuModeStr = "inefficient"; // 默认 on-CPU 模式
// 参数检查及帮助信息
if (argc > 1) {
if (strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0 || strcmp(argv[1], "-h") == 0) {
printUsage(argv[0]);
return 0;
}
}
if (argc > 1) { numThreads = atoi(argv[1]); }
if (argc > 2) { tasksPerThread = atoi(argv[2]); }
if (argc > 3) { cpuIterations = atoi(argv[3]); }
if (argc > 4) { ioDataSize = atoi(argv[4]); }
if (argc > 5) { ioWrites = atoi(argv[5]); }
if (argc > 6) { ioModeStr = argv[6]; }
if (argc > 7) { onCpuModeStr = argv[7]; }
// 根据 ioMode 参数决定当前 IO 模式
if (ioModeStr == "global") {
currentIOMode = IOMode::GLOBAL;
cout << "使用 GLOBAL 模式: 全局文件写入加全局互斥锁保护" << endl;
} else if (ioModeStr == "split") {
currentIOMode = IOMode::SPLIT;
cout << "使用 SPLIT 模式: 每个线程写入各自文件,降低锁粒度" << endl;
} else if (ioModeStr == "async") {
currentIOMode = IOMode::ASYNC;
cout << "使用 ASYNC 模式: 异步 IO,后台线程批量写入" << endl;
} else {
cout << "未知 IO 模式,默认使用 GLOBAL 模式" << endl;
currentIOMode = IOMode::GLOBAL;
}
// 根据 onCpuMode 参数决定 on-CPU 模式
if (onCpuModeStr == "efficient") {
efficientOnCpu = true;
cout << "采用高效的 on-CPU 写法" << endl;
} else {
efficientOnCpu = false;
cout << "采用劣化的 on-CPU 写法 (默认)" << endl;
}
int totalTasks = numThreads * tasksPerThread;
printDivider();
cout << "程序参数配置:" << endl;
cout << " 工作线程数 (numThreads): " << numThreads << endl;
cout << " 每个线程任务数 (tasksPerThread): " << tasksPerThread << endl;
cout << " 总任务数: " << totalTasks << endl;
cout << " On-CPU 计算迭代次数 (cpuIterations): " << cpuIterations << endl;
cout << " 单次 IO 写入数据字符数 (ioDataSize): " << ioDataSize << endl;
cout << " 单任务 IO 操作次数 (ioWrites): " << ioWrites << endl;
cout << " IO 模式 (ioMode): " << ioModeStr << endl;
cout << " on-CPU 模式 (onCpuMode): " << onCpuModeStr << endl;
printDivider();
// 根据 IO 模式进行必要初始化
if (currentIOMode == IOMode::GLOBAL) {
globalSyncFile.open("global_output.txt", ios::out | ios::trunc);
if (!globalSyncFile.is_open()){
cerr << "无法打开 global_output.txt 文件,请检查权限或路径。" << endl;
return 1;
}
} else if (currentIOMode == IOMode::ASYNC) {
asyncIO = new AsyncIOManager("async_output.txt", 50);
}
// 创建线程池、分发任务并测量总耗时
ThreadPool pool(numThreads);
auto startTime = high_resolution_clock::now();
for (int i = 0; i < totalTasks; i++) {
pool.enqueue([=]() {
processTask(i, cpuIterations, ioDataSize, ioWrites);
});
}
pool.wait();
auto endTime = high_resolution_clock::now();
duration<double> elapsed = endTime - startTime;
// 清理资源
if (currentIOMode == IOMode::GLOBAL) {
globalSyncFile.close();
} else if (currentIOMode == IOMode::ASYNC) {
delete asyncIO;
asyncIO = nullptr;
}
printDivider();
cout << "已完成 " << totalTasks << " 个任务,用时 "
<< fixed << setprecision(2) << elapsed.count() << " 秒。" << endl;
cout << "当前 IO 模式: " << ioModeStr << ", on-CPU 模式: " << onCpuModeStr << endl;
cout << "优化方向: 降低锁粒度/分散写入或采用批量异步 IO 能有效改善 off-CPU 瓶颈;" << endl;
cout << " on-CPU 部分即使采用高效写法,也不会显著影响总体运行时间." << endl;
printDivider();
return 0;
}

