ostringstream导致的TPS过低分析优化
发表于 2025/09/12
0
作者|陈兵
性能分析
demo代码如下:
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
std::string use_snprintf(int a) {
char buf[64];
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d", a);
return buf;
}
std::string use_stringstream(int a) {
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << a;
return oss.str();
}
const int LOOPS = 1000000;
void *thread(void *p) {
std::string (*foo)(int) = (std::string (*)(int))p;
for (int i = 0; i < LOOPS; ++i)
foo(i + 1);
return p;
}
double run_with_threads(int threads, std::string (*foo)(int)) {
timeval start, end;
gettimeofday(&start, nullptr);
pthread_t *tids = new pthread_t[threads];
for (int i = 0; i < threads; ++i)
pthread_create(&tids[i], nullptr, thread, (void *)foo);
for (int i = 0; i < threads; ++i)
pthread_join(tids[i], nullptr);
delete[] tids;
gettimeofday(&end, nullptr);
return (end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec) + (end.tv_usec - start.tv_usec) * 1e-6;
}
void test_with_threads(int threads) {
printf("%d threads:\n", threads);
double time_snprintf = run_with_threads(threads, use_snprintf);
double time_stringstream = run_with_threads(threads, use_stringstream);
printf("snprintf: %f\n", time_snprintf);
printf("stringstream: %f\n", time_stringstream);
printf("stream/snprintf: %f\n", time_stringstream / time_snprintf);
printf("\n");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc > 1) {
test_with_threads(atoi(argv[1]));
} else {
test_with_threads(1);
test_with_threads(2);
test_with_threads(4);
test_with_threads(10);
test_with_threads(20);
test_with_threads(30);
}
}
- 使用perf分析demo中的热点函数。
发现热点函数是一个locale类的构造函数、析构函数和赋值函数。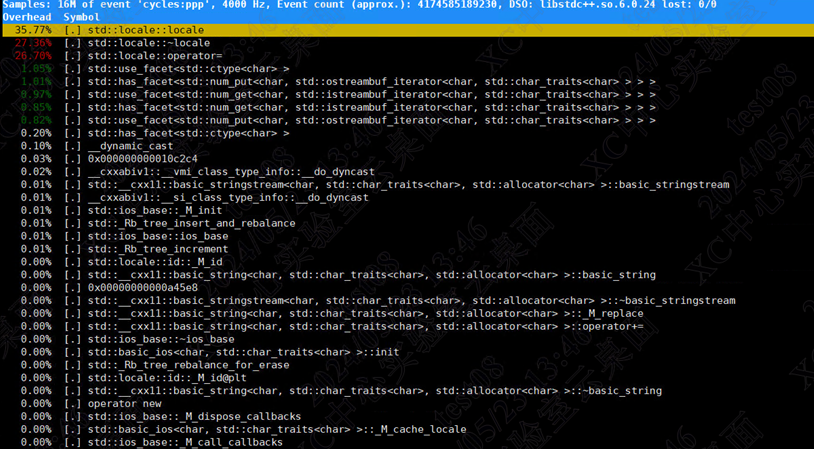
- 分析x86环境中demo的热点函数。
发现这三个函数性能占比很小,所以猜测ARM环境这三个函数在使用时存在问题。 - 尝试优化。
将locale类的创建放到demo函数use_snprintf中,运行程序发现果然use_snprintf和use_ stringstream的性能表现一致,都会差很多。再去单线程循环创建locale,发现性能与循环次数成线性关系,所以怀疑locale对象的创建销毁赋值等操作在多线程情况下存在资源竞争。 - 结合官网资料分析。
查阅了资料发现,在ostringstream对象的创建中,会创建新的locale对象。而locale是通过指针指向不同的facet全局对象来实现字符串格式化,所以创建locale本质上就是在创建新的指向facet对象的指针。并且每个facet对象会使用引用计数存储有多少个locale指向该facet对象,查看源码发现这里的引用计 - 数使用原子加减操作。
在ARM环境中,原子加减会使用ldxr/stxr指令(CAS的ARM实现),首先进行ldaxr对内存打上独占标志,然后做加减法,再将结果写回,但是如果在结果写回之前有线程已经对内存进行了写入,那么独占标志就会消失,本次线程结果作废,然后重新进行以上操作。在这个过程中,如果线程数以及物理核都比较多时,同一时刻就会有很多线程可以操作同一个资源,这个结果作废重新进行原子操作的次数就会变多,导致资源浪费。
性能优化
- 如果使用ostringstream的服务不是特别重的情况下,可以考虑进行绑核,人为限制物理核的使用个数,从而降低内存使用的竞争,这样也可以做到如x86一般性能和线程数成线性关系,但这样也可能因为限制了并发而造成服务性能下降。
- 使用高版本的G++(目前有试过G++ 10的版本),内部有对ostringstream的使用做优化。
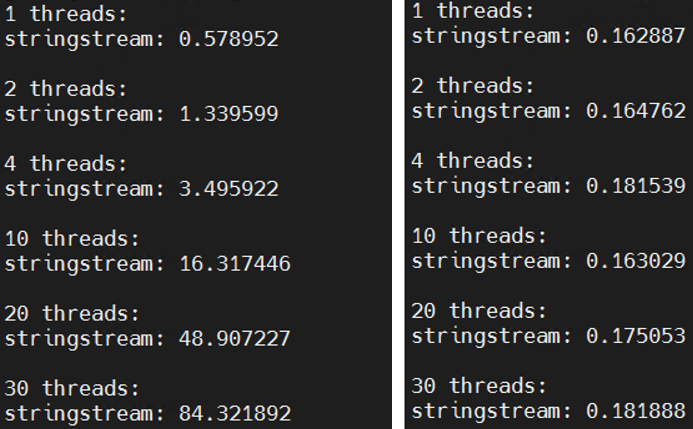
- 由于问题出现在并发循环创建ostringstream中,所以可以借助thread_local或者其余方式让单个线程复用同一个ostringstream对象,本身ostringstream网上资料也都是推荐进行资源复用的。修改代码让每个线程使用一个ostringstream,代码如下:
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
std::string use_stringstream(int a, std::ostringstream& oss) {
oss.str("");
oss << a;
return oss.str();
}
const int LOOPS = 1000000;
void *thread(void *p) {
std::string (*foo)(int, std::ostringstream&) = (std::string (*)(int, std::ostringstream&))p;
std::ostringstream oss;
for (int i = 0; i < LOOPS; ++i)
foo(i + 1, oss);
return p;
}
double run_with_threads(int threads, std::string (*foo)(int, std::ostringstream&)) {
timeval start, end;
gettimeofday(&start, nullptr);
pthread_t *tids = new pthread_t[threads];
for (int i = 0; i < threads; ++i)
pthread_create(&tids[i], nullptr, thread, (void *)foo);
for (int i = 0; i < threads; ++i)
pthread_join(tids[i], nullptr);
delete[] tids;
gettimeofday(&end, nullptr);
return (end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec) + (end.tv_usec - start.tv_usec) * 1e-6;
}
void test_with_threads(int threads) {
printf("%d threads:\n", threads);
double time_stringstream = run_with_threads(threads, use_stringstream);
printf("stringstream: %f\n", time_stringstream);
printf("\n");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc > 1) {
test_with_threads(atoi(argv[1]));
} else {
test_with_threads(1);
test_with_threads(2);
test_with_threads(4);
test_with_threads(10);
test_with_threads(20);
test_with_threads(30);
}
} - 修改后的代码性能很高,性能损耗基本与线程数无关,当线程数较多时能提高几百倍的性能。