KBest算法替换Faiss(HNSW)进行向量检索
发表于 2025/06/12
0
背景介绍
Faiss(HNSW)
Faiss是由facebook开发的用于高效相似搜索和密集向量聚类的算法库,其核心采用C++编写,并为Python/numpy提供完整封装接口。Faiss提供Flat、IVFFlat、PQ、IVFPQ、HNSW等索引方式,其中HNSW参考Efficient and robust approximate nearest neighbor search using Hierarchical Navigable Small World graphs实现。
HNSW(Hierarchical Navigable Small World,分层可导航小世界图)是一种高效的近似最近邻搜索(ANN)算法,其核心思想是通过构建多层图结构来加速高维空间中的相似性搜索。
KBest
KBest(Kunpeng Blazing-fast embedding similarity search thruster)鲲鹏图检索算法,是鲲鹏自研的高效的图检索算法,核心采用C++编写,并为Python提供完整封装接口。通过量化、NUMA访存调度等方法优化了最近邻搜索的性能和精度,适用于鲲鹏920新型号处理器。KBest支持两种不同的构建k近邻图的算法,RNNDescent和NNDescent,支持四种不同的选择邻居策略HNSW、NSG、TSDG、SSG。
准备工作
本文基于鲲鹏920新型号处理器进行方法介绍,使用KBest 1.2.0替换Faiss(HNSW) 1.8.0进行向量相似搜索。
配置环境
已验证环境:
| 操作系统 | CPU类型 | 内存 | 编译器 | CMake | GLIBCXX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| openEuler 22.03 LTS SP3 | 鲲鹏920新型号处理器 | 16 * 32G | GCC 10.3.1 | >=3.22.0 | >=3.4.28 |
安装Faiss
步骤1 获取OpenBLAS源代码
假设代码存放路径为/path/to/openblas。
cd /path/to/openblas
git clone https://github.com/OpenMathLib/OpenBLAS.git -b v0.3.29步骤2 编译安装OpenBLAS
cd OpenBLAS
make
make install
# 可选make install PREFIX=your_installation_directory指定安装路径,默认路径为/opt/OpenBLAS步骤3 获取Faiss源代码
假设代码存放路径为/path/to/faiss。
cd /path/to/faiss
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/faiss.git -b v1.8.0步骤4 编译安装Faiss。
cd faiss
cmake -B build . \
-DFAISS_ENABLE_GPU=OFF \
-DBUILD_TESTING=OFF \
-DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-DFAISS_OPT_LEVEL=generic \
-DFAISS_ENABLE_PYTHON=OFF \
-DMKL_LIBRARIES=/opt/OpenBLAS/lib/libopenblas.so # 注意此处修改为实际OpenBLAS安装的路径
make -C build -j faiss
make -C build install
# 默认安装路径为/usr/local安装KBest
步骤1 获取软件包
从华为企业业务网站鲲鹏社区获取对应的软件数字证书和软件安装包。软件包名称为BoostKit-SRA_Recall_xxxx.zip,用户解压zip文件后可获取RPM安装包,其中xxxx代表版本号。
软件包获取地址:鲲鹏社区
使用软件包前请先阅读:鲲鹏应用使能套件BoostKit用户许可协议 2.0,如确认继续使用,则默认同意协议的条款和条件。
步骤2 软件包完整性检查
校验工具和校验方法获取地址:https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/zh/tool/pgp-verify-TL1000000054
请参见《OpenPGP签名验证指南》进行软件包完整性检查。
步骤3 安装软件包
rpm -ivh boostkit-sra_recall-xxxx.aarch64.rpm上述命令中涉及的xxxx代表版本号。安装结束后,自动追加环境变量LD_LIBRARY_PATH到/etc/profile中,即KBest的动态库文件所在目录/usr/local/sra_recall/lib。
步骤4 安装后验证
执行source命令或重新登录终端使环境变量生效。
source /etc/profile查看环境变量LD_LIBRARY_PATH是否包含KBest的安装路径/usr/local/sra_recall/lib。
env | grep LD_LIBRARY_PATH如果变量包含安装路径,说明安装成功。安装成功后在安装路径(默认路径是/usr/local/sra\_recall)下生成相应文件,其中,include文件夹包含KBest的头文件,lib文件夹包含了KBest的动态库文件。
安装其他依赖
yum install hdf5 hdf5-devel numactl numactl-devel
替换方法
测试流程以开源数据集sift-128-euclidean.hdf5为例。测试程序采用单进程80线程的完全并行架构,所有线程同时发起向量查询请求以模拟高并发场景。
假设KBest测试路径为/path/to/kbest,Faiss(HNSW)测试路径为/path/to/faiss-hnsw。
数据准备
在/path/to/kbest与/path/to/faiss-hnsw文件夹下创建data文件夹用于存放数据集。
mkdir data && cd data
wget http://ann-benchmarks.com/sift-128-euclidean.hdf5 --no-check-certificate定义数据集类,用于处理数据集信息。此处KBest与Faiss(HNSW)方法一致。
// 定义数据集类,用于处理数据集信息
class Datasets {
public:
std::string path;
std::string dataset_name;
size_t d; // 向量维度
size_t nb; // 底库向量数量
size_t nq; // 查询向量数量
size_t nq2; // 真实最近邻对应的查询数量
size_t k; // 查询点的真实最近邻数量
size_t topk; // 需要检索的数量
float *xb = nullptr; // 底库向量
float *xq = nullptr; // 查询向量
int64_t *gt = nullptr; // 查询点的真实最近邻索引
Datasets(std::string &_p, std::string &_name, size_t _k, bool type)
: path(_p + _name),
topk(_k),
dataset_name(_name)
{
char fname[100];
strcpy(fname, path.c_str());
H5File file(fname, H5F_ACC_RDONLY);
char p[100];
strcpy(p, "train");
xb = hdf5_read_floats(&file, p, &nb, &d);
size_t d2;
strcpy(p, "test");
xq = hdf5_read_floats(&file, p, &nq, &d2);
strcpy(p, "neighbors");
int *gt_int = hdf5_read_ints(&file, p, &k, &nq2);
gt = new int64_t[topk * nq];
for (int i = 0; i < nq; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < topk; j++) {
gt[i * topk + j] = gt_int[i * k + j];
}
}
delete[] gt_int;
assert(nq == nq || !"Ground truth size mismatch!");
}
~Datasets()
{
delete[] xb;
delete[] xq;
delete[] gt;
}
// 对向量进行归一化处理(IP数据集需要)
void normalize(float *vectors, size_t n, size_t d)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
float norm = 0.0f;
for (size_t j = 0; j < d; j++) {
norm += vectors[i * d + j] * vectors[i * d + j];
}
norm = std::sqrt(norm);
if (norm > 0) {
for (size_t j = 0; j < d; j++) {
vectors[i * d + j] /= norm;
}
}
}
}
// 从HDF5文件中读取浮点数数据
float *hdf5_read_floats(H5File *file, const char *fname, size_t *n_out, size_t *d_out)
{
try {
DataSet dataset = file->openDataSet(fname);
DataSpace dataspace = dataset.getSpace();
hsize_t dims[2];
dataspace.getSimpleExtentDims(dims, nullptr);
*n_out = dims[0];
*d_out = dims[1];
float *data = new float[*n_out * *d_out];
dataset.read(data, PredType::NATIVE_FLOAT);
return data;
} catch (const FileIException &e) {
cerr << "File open error: " << e.getDetailMsg() << endl;
exit(1);
} catch (const DataSetIException &e) {
cerr << "Dataset open error: " << e.getDetailMsg() << endl;
exit(1);
} catch (const DataSpaceIException &e) {
cerr << "Dataspace error: " << e.getDetailMsg() << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
// 从HDF5文件中读取整数数据
int *hdf5_read_ints(H5File *file, const char *fname, size_t *d_out, size_t *n_out)
{
try {
DataSet dataset = file->openDataSet(fname);
DataSpace dataspace = dataset.getSpace();
hsize_t dims[2];
dataspace.getSimpleExtentDims(dims, nullptr);
*n_out = dims[0];
*d_out = dims[1];
int *data = new int[*n_out * *d_out];
dataset.read(data, PredType::NATIVE_UINT);
return data;
} catch (const FileIException &e) {
cerr << "File open error: " << e.getDetailMsg() << endl;
exit(1);
} catch (const DataSetIException &e) {
cerr << "Dataset open error: " << e.getDetailMsg() << endl;
exit(1);
} catch (const DataSpaceIException &e) {
cerr << "Dataspace error: " << e.getDetailMsg() << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
};测试结果处理
定义测试结果类,用于存储和处理测试结果。此处KBest与Faiss(HNSW)方法一致。
// 定义测试结果类,用于存储和处理测试结果
class TestResult {
public:
double recall;
double calculate_quantity;
double total_time;
std::vector<double> search_time;
TestResult()
: total_time(0), recall(0), calculate_quantity(0) {
search_time.clear();
accumulate_time.clear();
}
~TestResult()
{
search_time.clear();
accumulate_time.clear();
}
// 对搜索时间进行排序并计算累积时间
void reorder()
{
if (search_time.size() > 0) {
std::sort(search_time.begin(), search_time.end());
accumulate_time.clear();
accumulate_time.push_back(0);
for (size_t i = 0; i < search_time.size(); ++i) {
accumulate_time.push_back(accumulate_time.back() + search_time[i]);
}
}
}
double get_total(int begin, int end)
{
if (begin >= 0 && end < accumulate_time.size() && begin < end) {
return accumulate_time[end] - accumulate_time[begin];
}
return 0;
}
private:
std::vector<double> accumulate_time;
};单线程搜索
定义KBest与Faiss(HNSW)搜索时的参数结构体,实现单线程搜索功能,以满足后续并发场景的实现。
Faiss(HNSW)
pthread_mutex_t mtx; // 互斥锁,防止多线程竞争
pthread_cond_t cond; // 条件变量,用于线程间的条件等待和通知机制
int ready = 0; // 线程启动就绪标志
// 执行搜索操作
void search(const faiss::IndexHNSWFlat *index, const Datasets *data, faiss::idx_t *I, float *D, int offset = 0,
int nq = 1, const faiss::SearchParameters *params = nullptr)
{
index->search(nq, data->xq + offset * data->d, data->topk, D + offset * data->topk, I + offset * data->topk,
params);
}
// 定义线程相关的全局变量
struct HNSWSearchParams {
const faiss::IndexHNSWFlat *index; // Faiss(HNSW)索引对象
const Datasets *data; // 数据集信息
faiss::idx_t *I; // 输出:最近邻的索引数组
float *D; // 输出:最近邻的距离数组
const faiss::SearchParameters *faiss_params; // Faiss(HNSW)搜索参数
int nq; // 查询向量数量
int offset; // 查询向量的起始偏移量
};
// 单线程搜索函数
void *search_single_thread(void *arg)
{
HNSWSearchParams *params = static_cast<HNSWSearchParams *>(arg);
int nq = params->nq;
int offset = params->offset;
int d = params->data->d;
int topk = params->data->topk;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);
// Faiss(HNSW)使用OMP,此处调整线程
omp_set_num_threads(1);
while (ready == 0) {
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mtx);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);
for (int i = 0; i < nq; i++) {
params->index->search(1, params->data->xq + (offset + i) * d, topk, params->D + (offset + i) * topk,
params->I + (offset + i) * topk, params->faiss_params);
}
return nullptr;
}KBest
extern bool NUMA_ENABLED; // 是否开启NUMA优化
extern int num_numa_nodes; // 使用的NUMA节点数量
pthread_mutex_t mtx; // 互斥锁,防止多线程竞争
pthread_cond_t cond; // 条件变量,用于线程间的条件等待和通知机制
int ready = 0; // 线程启动就绪标志
std::unique_ptr<KBest> best_build = nullptr; // KBest索引对象
// 定义线程相关的全局变量
struct KBestSearchParams {
const Datasets *data; // 数据集对象
int n; // 查询向量数量
const float* x; // 查询向量
int k; // 最近邻的数量。
float* D; // 输出:最近邻的距离数组
int64_t* I; // 输出:最近邻的索引数组
int dim; // 向量维度
};
// 单线程搜索函数
void *search_single_thread(void* arg)
{
KBestSearchParams* params = static_cast<KBestSearchParams*>(arg);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);
while (ready == 0) {
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mtx);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);
for (int i = 0; i < params->n; i++) {
best_build->Search(1, params->x + i * params->dim, params->k, params->D + i * params->k, params->I + i * params->k, 1);
}
return nullptr;
}并发搜索及结果计算
Faiss(HNSW)相关C++ API详细说明可见Struct faiss::IndexHNSWFlat,KBest相关C++ API详细说明可见KBest C++接口说明。
Faiss(HNSW)
/**
* @param data 数据集对象
* @param k_f Faiss(HNSW)构建参数:邻居节点数
* @param tr TestResult对象,用于存储测试结果
* @param nloop 测试循环次数
* @param efs Faiss(HNSW)搜索参数:候选节点列表大小
* @param efc Faiss(HNSW)构建参数:候选节点列表大小
* @param num_threads 并发线程数
* @param metric Faiss(HNSW)构建参数:距离度量类型
*/
void accu_qps(const Datasets *data, int k_f, TestResult *tr, const int nloop, const int efs, const int efc,
const int num_threads, faiss::MetricType metric)
{
double timeElapsed = 0;
struct timespec startTime;
struct timespec endTime;
// 构建Faiss(HNSW)索引并记录时间
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &startTime);
faiss::IndexHNSWFlat index(data->d, k_f, metric);
index.hnsw.efConstruction = efc;
index.add(data->nb, data->xb);
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &endTime);
timeElapsed += (endTime.tv_sec - startTime.tv_sec) + 1e-9 * (endTime.tv_nsec - startTime.tv_nsec);
faiss::SearchParametersHNSW faiss_params;
faiss_params.efSearch = efs;
// 分配结果存储空间(距离D和索引I)
faiss::idx_t *I = new faiss::idx_t[data->topk * data->nq * num_threads];
float *D = new float[data->topk * data->nq * num_threads];
printf("accu_qps, nloop:%d, threads:%d\n", nloop, num_threads);
int nq = data->nq;
int32_t base_num_queries = nq / num_threads;
int32_t left = nq % num_threads;
// 计算每个线程的查询偏移量(用于分块处理)
std::vector<int> thread_offset(num_threads + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; ++i) {
if (i < left) {
thread_offset[i + 1] = base_num_queries + 1;
} else {
thread_offset[i + 1] = base_num_queries;
}
}
// 多轮测试循环
for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; ++i) {
thread_offset[i + 1] += thread_offset[i];
}
// 创建线程并分配任务
for (int i = 0; i < nloop; i++) {
pthread_mutex_init(&mtx, nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&cond, nullptr);
ready = false;
std::vector<pthread_t> threads(num_threads);
std::vector<HNSWSearchParams> params(num_threads);
for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; ++i) {
params[i].index = (&index);
params[i].data = data;
params[i].I = I + data->topk * data->nq * i;
params[i].D = D + data->topk * data->nq * i;
params[i].nq = params[i].data->nq;
params[i].offset = 0;
params[i].faiss_params = (&faiss_params);
pthread_create(&threads[i], nullptr, search_single_thread, ¶ms[i]);
}
// 等待所有线程初始化完成
sleep(2);
// 启动所有线程并计时
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);
ready = 1;
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &startTime);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);
// 等待所有线程完成
for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; i++) {
pthread_join(threads[i], NULL);
}
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &endTime);
timeElapsed = (endTime.tv_sec - startTime.tv_sec) + 1e-9 * (endTime.tv_nsec - startTime.tv_nsec);
tr->search_time.push_back(timeElapsed);
tr->total_time += timeElapsed;
std::cout << "Loop " << i + 1 << "/" << nloop << ": Search time = " << timeElapsed << " s"
<< ", QPS = " << data->nq / timeElapsed << std::endl;
}
tr->calculate_quantity = data->nq;
std::cout << "search total cost time: " << tr->total_time << " s" << std::endl;
// 计算召回率(Recall)
int n_10 = 0;
for (int iq = 0; iq < data->nq; iq++) {
for (int i = 0; i < data->topk; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < data->topk; j++) {
if (I[iq * data->topk + j] == data->gt[iq * data->topk + i]) {
n_10++;
}
}
}
}
tr->recall = (n_10 / float(data->nq) / 10.);
tr->reorder();
std::cout << "search average cost time: " << tr->total_time / nloop << " s" << std::endl;
delete[] I;
delete[] D;
}
std::pair<double, double> test(std::string &path, std::string &dataset_name, int factor, bool is_euclidean,
const int nloop, const int efs, const int efc, int num_threads, faiss::MetricType metric)
{
TestResult tr;
Datasets data(path, dataset_name, 10, is_euclidean);
printf("base vector size: %d\n", data.nb);
printf("query vector size: %d\n", data.nq);
accu_qps(&data, factor, &tr, nloop, efs, efc, num_threads, metric);
std::cout << "==================================================" << std::endl;
int begin_id = nloop / 4;
int end_id = nloop * 3 / 4;
double qps = tr.calculate_quantity / tr.get_total(begin_id, end_id) * (end_id - begin_id);
std::cout << "Fianl Results: "
<< "qps " << qps << " recall " << tr.recall << std::endl;
return std::make_pair(qps, tr.recall);
}KBest
/**
* @param data 数据集对象
* @param k_f KBest构建参数:邻居节点数
* @param tr TestResult对象,用于存储测试结果
* @param nloop 测试循环次数
* @param efs KBest搜索参数:候选节点列表大小
* @param efc KBest构建参数:候选节点列表大小
* @param num_threads 并发线程数
* @param A KBest构建参数:构图剪枝时的角度阈值
* @param graph_opt_iter KBest构建参数:图优化迭代次数
* @param metric KBest构建参数:距离度量类型
* @param init_builder_type KBest构建参数:构建k近邻图的算法
* @param index_type KBest构建参数:选择邻居策略
* @param consecutive KBest构建参数:块大小
* @param reorder KBest构建参数:是否开启底库向量重排
* @param level KBest构建参数:控制量化的等级
* @param adding_pref KBest搜索参数:超参候选集插入阈值
* @param patience KBest搜索参数:检索耐心值
*/
void accu_qps(const Datasets *data, int k_f, TestResult *tr, const int nloop, const int efs, const int efc,
const int num_threads, int A, int graph_opt_iter, const char *metric,
const std::string &init_builder_type, const std::string &index_type, int consecutive, int reorder,
int level, int adding_pref, int patience) {
double timeElapsed = 0;
struct timespec startTime, endTime;
// 构建KBest索引并记录时间
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &startTime);
best_build = std::make_unique<KBest>(data->d, k_f, efc, A, graph_opt_iter, metric, init_builder_type, index_type);
best_build->Add(data->nb, data->xb, consecutive, reorder, level); // 构建图索引
best_build->BuildSearcher(); // 构建检索器
best_build->SetEf(efs); // 设置检索时的候选节点列表大小
best_build->SetEarlyStoppingParams(adding_pref, patience); // 设置早停参数
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &endTime);
timeElapsed += (endTime.tv_sec - startTime.tv_sec) + 1e-9 * (endTime.tv_nsec - startTime.tv_nsec);
// 分配结果存储空间(距离D和索引I)
float *D = new float[data->topk * data->nq * num_threads];
int64_t *I = new int64_t[data->topk * data->nq * num_threads];
printf("accu_qps, nloop:%d, threads:%d\n", nloop, num_threads);
int nq = data->nq;
int32_t base_num_queries = nq / num_threads;
int32_t left = nq % num_threads;
// 计算每个线程的查询偏移量(用于分块处理)
std::vector<int> thread_offset(num_threads + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; ++i) {
thread_offset[i + 1] = (i < left) ? base_num_queries + 1 : base_num_queries;
thread_offset[i + 1] += thread_offset[i];
}
// 多轮测试循环
for (int i = 0; i < nloop; i++) {
pthread_mutex_init(&mtx, nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&cond, nullptr);
ready = false;
// 创建线程并分配任务
std::vector<pthread_t> threads(num_threads);
std::vector<KBestSearchParams> params(num_threads);
for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; ++i) {
params[i].data = data;
params[i].n = thread_offset[i + 1] - thread_offset[i];
params[i].x = data->xq + thread_offset[i] * data->d;
params[i].k = data->topk;
params[i].dim = data->d;
params[i].D = D + data->topk * thread_offset[i];
params[i].I = I + data->topk * thread_offset[i];
pthread_create(&threads[i], nullptr, search_single_thread, ¶ms[i]);
}
// 等待所有线程初始化完成
sleep(2);
// 启动所有线程并计时
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);
ready = 1;
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &startTime);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);
// 等待所有线程完成
for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; i++) {
pthread_join(threads[i], NULL);
}
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &endTime);
timeElapsed = (endTime.tv_sec - startTime.tv_sec) + 1e-9 * (endTime.tv_nsec - startTime.tv_nsec);
tr->search_time.push_back(timeElapsed);
tr->total_time += timeElapsed;
std::cout << "Loop " << i + 1 << "/" << nloop << ": Search time = " << timeElapsed << " s"
<< ", QPS = " << data->nq / timeElapsed << std::endl;
}
// 计算召回率(Recall)
int n_10 = 0;
for (int iq = 0; iq < data->nq; iq++) {
for (int i = 0; i < data->topk; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < data->topk; j++) {
if (I[iq * data->topk + j] == data->gt[iq * data->topk + i]) {
n_10++;
}
}
}
}
tr->recall = (n_10 / float(data->nq) / 10.;
tr->reorder();
std::cout << "search average cost time: " << tr->total_time / nloop << " s" << std::endl;
delete[] I;
delete[] D;
}
std::pair<double, double> test(std::string &path, std::string &dataset_name, int factor, bool is_euclidean,
const int nloop, const int efs, const int efc, int num_threads, int A, int graph_opt_iter,
const char *metric, const std::string &init_builder_type, const std::string &index_type,
int consecutive, int reorder, int level, int adding_pref, int patience)
{
TestResult tr;
Datasets data(path, dataset_name, 10, is_euclidean);
printf("base vector size: %d\n", data.nb);
printf("query vector size: %d\n", data.nq);
accu_qps(&data, factor, &tr, nloop, efs, efc, num_threads, A, graph_opt_iter, metric, init_builder_type, index_type,
consecutive, reorder, level, adding_pref, patience);
std::cout << "==================================================" << std::endl;
int begin_id = nloop / 4;
int end_id = nloop * 3 / 4;
double qps = tr.calculate_quantity / tr.get_total(begin_id, end_id) * (end_id - begin_id);
std::cout << "Fianl Results: "
<< "qps " << qps << " recall " << tr.recall << std::endl;
return std::make_pair(qps, tr.recall);
}包含头文件及主函数
给定构建及检索时的参数,进行测试。
Faiss(HNSW)
#include <cstdio> #include <cassert> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <omp.h> #include <H5Cpp.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <faiss/IndexHNSW.h>using namespace H5; using namespace std;
int main()
{
std::string dataset = "sift-128-euclidean.hdf5";
std::string path = "data/";
int M = 24;
int efConstruction = 100;
int efSearch = 200;
bool is_euclidean = true;
const int nloop = 5;
int num_threads = 80;
faiss::MetricType metric = faiss::METRIC_L2;
printf("Now test Faiss(HNSW) with dataset %s!\n", dataset.c_str());
test(path, dataset, M, is_euclidean, nloop, efSearch, efConstruction, num_threads, metric);
return 0;
}KBest
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <numa.h> #include <iostream> #include <memory> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "hdf5.h" #include <H5Cpp.h> #include "kbest.h"using namespace H5; using namespace std;
int main()
{
std::string dataset = "sift-128-euclidean.hdf5";
std::string path = "data/";
int M = 50;
int efConstruction = 300;
int efSearch = 96;
bool is_euclidean = true;
const int nloop = 5;
int num_threads = 80;
int A = 1;
int graph_opt_iter = 0;
const char *metric = "L2";
std::string init_builder_type = "RNNDescent";
std::string index_type = "TSDG";
int consecutive = 20;
int reorder = 1;
int level = 0;
int adding_pref = 23;
int patience = 32;
NUMA_ENABLED = false;
printf("Now test KBest with dataset %s!\n", dataset.c_str());
test(path, dataset, M, is_euclidean, nloop, efSearch, efConstruction, num_threads, A, graph_opt_iter, metric,
init_builder_type, index_type, consecutive, reorder, level, adding_pref, patience);
return 0;
}编译及运行
假设以上代码整合后放于/path/to/faiss-hnsw/hnsw_test.cpp与/path/to/kbest/kbest_test.cpp。
Faiss(HNSW)
# 注意此处替换为OpenBLAS和Faiss的实际安装路径
g++ -std=c++11 hnsw_test.cpp -L/usr/local/lib64/ -L/opt/OpenBLAS/lib -lfaiss -lstdc++ -lhdf5_cpp -lhdf5 -fopenmp -o hnsw_test
./hnsw_testKBest
g++ -std=c++17 -fPIC -Ofast -march=armv8.2-a+dotprod kbest_test.cpp -I/usr/local/sra_recall/include -L/usr/local/sra_recall/lib -lkbest -lhdf5_cpp -lhdf5 -lnuma -o kbest_test
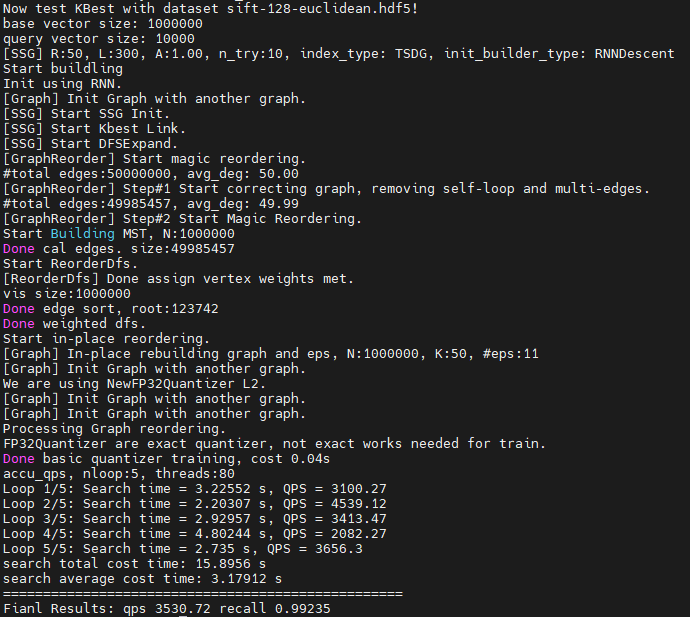
./kbest_test测试结果
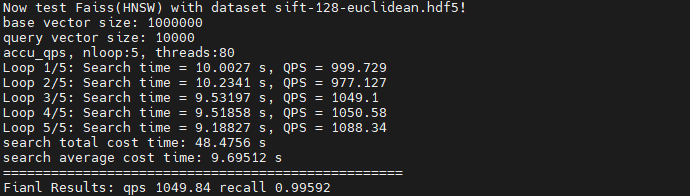
Faiss(HNSW)
KBest